Natural disasters such as storms, earthquakes and wildfires are widely recognized for their devastating economic impacts. A new study released on March 17, 2023, revealed that biological invasions from invasive species are as economically devastating as these more well-known phenomena, underscoring the importance of action and preventative measures.
Invasive species – organisms introduced by humans to new environments that harm the environment, economy, and society – are a growing problem worldwide. Invasive species cause socio-economic harm through damaging or altering access to infrastructure, such as when zebra and quagga mussels clog water intake pipes or invasive aquatic plants form dense mats of vegetation that impede recreational access to waterways. Economically important natural resources such as commercial and sport fisheries may also be threatened when invasive species impact wildlife populations.

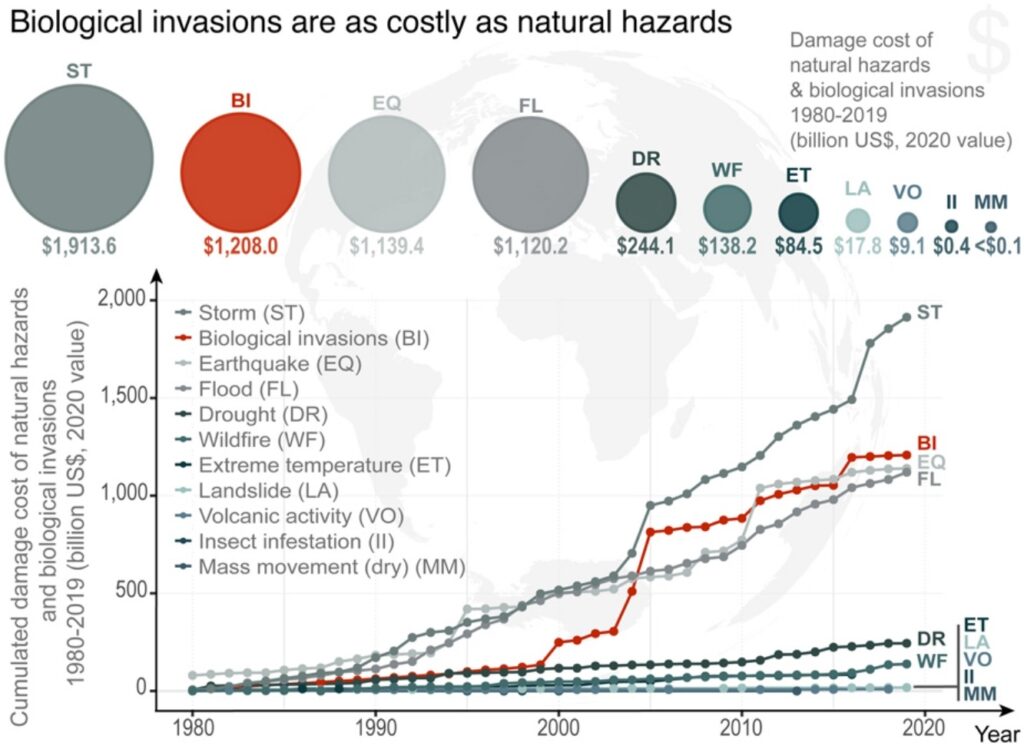
“Our findings revealed that the global economic losses from biological invasions, which may typically be considered as a slow-onset hazard, were in the same order of magnitude as economic losses from storms and earthquakes, amounting to $1,208 billion (USD). These impacts are cumulative and profound, including species extinctions, massive costs, and even human deaths,” said Dr. Anna Turbelin.
Costs of biological invasions are steep, and they are only expected to increase in the coming years, driven by factors such as climate change and increased international trade and travel. Related to this, the study found that invasion costs increased faster than natural hazard costs over time with a 702% increase in reported losses between the periods of 1980 – 1999 and 2000 -2019.
“This new research reveals the impacts of invasive species are as costly as natural disasters such as storms and earthquakes, further emphasizing the need to strengthen measures to prevent and manage invasive species through increased mapping, monitoring, reporting, and response to protect lakes, lands, communities, and the economy,” said Sarah Rang, Executive Director of the Invasive Species Centre.
“Societies need to build a culture of safety and resilience against the threat of invasive species”,
recommends Dr. Anthony Ricciardi, McGill University. “Just like we reinforce infrastructure and develop
emergency response plans against earthquakes and other extreme natural hazards, we should adopt
similar precautionary approaches to prevent biological invasions.”
Several things can be done to minimize the impacts of invasive species and action can take place at all levels of society. Decision-makers can make policy changes to reflect management needs and direct resources to relevant programs. Environmental and land managers can take steps to prevent, manage and eradicate invasive species through their work. Community members can prevent the spread of invasive species by fully cleaning vehicles, gear, clothing, and footwear when they are out in nature.
The public can also help by reporting invasive species sightings on apps like EDDMapS and iNaturalist, spreading the word on invasive species prevention, and even participating in stewardship events such as invasive species pulls or community science monitoring activities.
About InvaCost
InvaCost is a global, online database created to harmonize data on the cost of worldwide biological invasions. It uses a systematic, standardized methodology to collect information from peer-reviewed articles and grey literature. It has been a valuable source of data for several analyses on the economic impacts of invasive species.
